Menus¶
A menu is a selection of options from which an operator can choose the next action to occur in a program. Two menu styles are supported. Only one menu style may be used in any individual program.
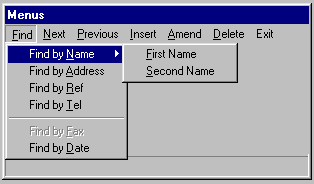
The drop menu style is the recommended method. Each top level window defined in a program may have a menu of its own. The menu consists of a number of menu items, each of which, when selected, causes a different section of code to be executed. Certain menu items are themselves menus; when an item of this type is selected a further submenu appears, with items of its own. Submenus may be nested indefinitely. A typical drop menu, with two levels of submenu opened, is shown in the illustration.
The main menu items are displayed in a menu bar, positioned at the top of the window, Subitems drop down in a window beneath their parent item.
Menu items can be enabled or disabled while a program is running, and accelerator keys and hotkeys can be assigned to items to maximise ease and speed of selection.
Unless otherwise specified, references to menus in these helpfiles mean drop menus.
A popup menu is a drop menu that can be opened at any location in the parent window; this is most commonly generated by the user right-clicking the mouse over a window or control.
The ring menu style consists of a single line of options positioned at the top of the screen. A single ring menu must suffice for every window within the program, and options cannot be disabled or enabled. Ring menus, though much less flexible than drop menus, can be coded very quickly and can therefore be useful during testing.
MENU TOPICS
RELATED TOPICS |